Interweaving Online Media with IxIF

Photo by Robert Sanderson (Stanford)
On 6-8 April members of the IIIF community met at the British Library in London to discuss and define preliminary specifications for a new framework that will support and serve audiovisual content, extending the current image content platform. The Netherlands Institute for Sound & Vision was there, represented by Themistoklis Karavellas.
What is the IIIF community?
IIIF stands for International Image Interoperability Framework. In its essence, it's a community of people and institutions that came together to create specifications/web APIs, implement them, and use them to provide access to rich media content. IIIF is the resulting framework, already implemented and used in providing access to images.
The building blocks comprising it are:
- The Image API - gives access to pixels, and supports various methods of visual content transformations.
Photo by Europeana Tech Insight.
- The Presentation API - gives information about how to present, arrange, annotate, reuse IIIF content.
Photo by Europeana Tech Insight.
- The Search API (in Beta) - provides search functionality over a set of annotations.
- The Authentication API (in Beta) - provides authorization functionality in case the content should be protected.
So, what is the IxIF?
Many people participating in the IIIF community come from organizations where a lot more than only images are stored in their archives. Therefore, the framework needs to be extended to support a surplus of rich media content such as video, audio and born digital files. Thus, as part of a next step of work in the community, the "Image" part of the framework title will be replaced by something new, for the moment the unknown-X. An example case of this functionality was developed and published by Tom Crane.
Why is the Netherlands Institute of Sound & Vision (NISV) interested?
NISV collects, preserves and opens the audiovisual archive of the Netherlands.This translate to over 1 million hours of video, images, audio recordings, etc. IIIF and IxIF could be used as an effective, flexible and standardised framework for providing access to our content.
In more detail, the use cases of interest for NISV are:
- Standardised way of presenting (open) video and audio content:
- What players should/could support IxIF?
- What would be the compatibility with current web standards (HTML5)?
- How to include subtitling? - Citation and sharing of audiovisual content.
- Methods for relating cited fragments to other items and collections (hierarchical relations & contextualisation).
- Annotations:
- Different levels of annotations: crowd, automatic, manual.
- Different provenance & authority for each layer.
- Question: What is the relation with the Web Annotation Model and/or Open Annotations (or W3C initiatives around data modeling in general)? - Content security.
- Translation / multilinguality.
What was discussed?
Following IIIF's iterative process for introducing new specifications to the framework, each one of the workshop's participants came up with a number of use cases from his/her own organization and domain of expertise. The use cases were presented to the group and the order of the topics in discussion was decided based on the interest level within the whole group for each one of them.
The use cases discussed during the workshop:
- Get access to a full video/audio stream and play it
- Ability to control playback
- Access via mobile (responsive), or embedded on a page
- Meeting accessibility requirements
- Ability to refer to a point in time
- Variant: Segmentation of video, audio by time - Ability to snip a segment of a recording for download
- Internationalization
- Downloading a still frame from video as image
- Data analysis of subset of a file
- Reference to a spatial bounding box (by area)
- Drawing on the video
- Segmentation of video by region
- Gapless playback ( serial delivery of multiple files for a single recording)
- Different streams play-out with a gap (describing the gap)
- Synchronization of video/audio stream and subtitles
- Increasing / decreasing audio delay
- Slideshow view of images with audio
- Working with audio manifest only
- Thumbnails of audio/video
- Linking to other objects in the collection
- Creation of "packages" that include audio + image + PDF etc.
- Playback (audio and video) at different speeds
- Description of media type, aspect ratio and resolution
- Virtual timeline to annotate across media resources
- Ability to describe navigation and hierarchy
- Display rights / license / attribution along with content
- Full text search of transcribed speech
- Authenticated access to video/audio
- Zooming into videos
Additional use cases together with the extensive descriptions of the cases mentioned above can be found in the notes of the workshop.
Participants' Demos
A very interesting part of the workshop were the demo presentations some of the participants had prepared. Though these presentations it was easier to understand the use cases presented and the functionalities that should be supported in IxIF.
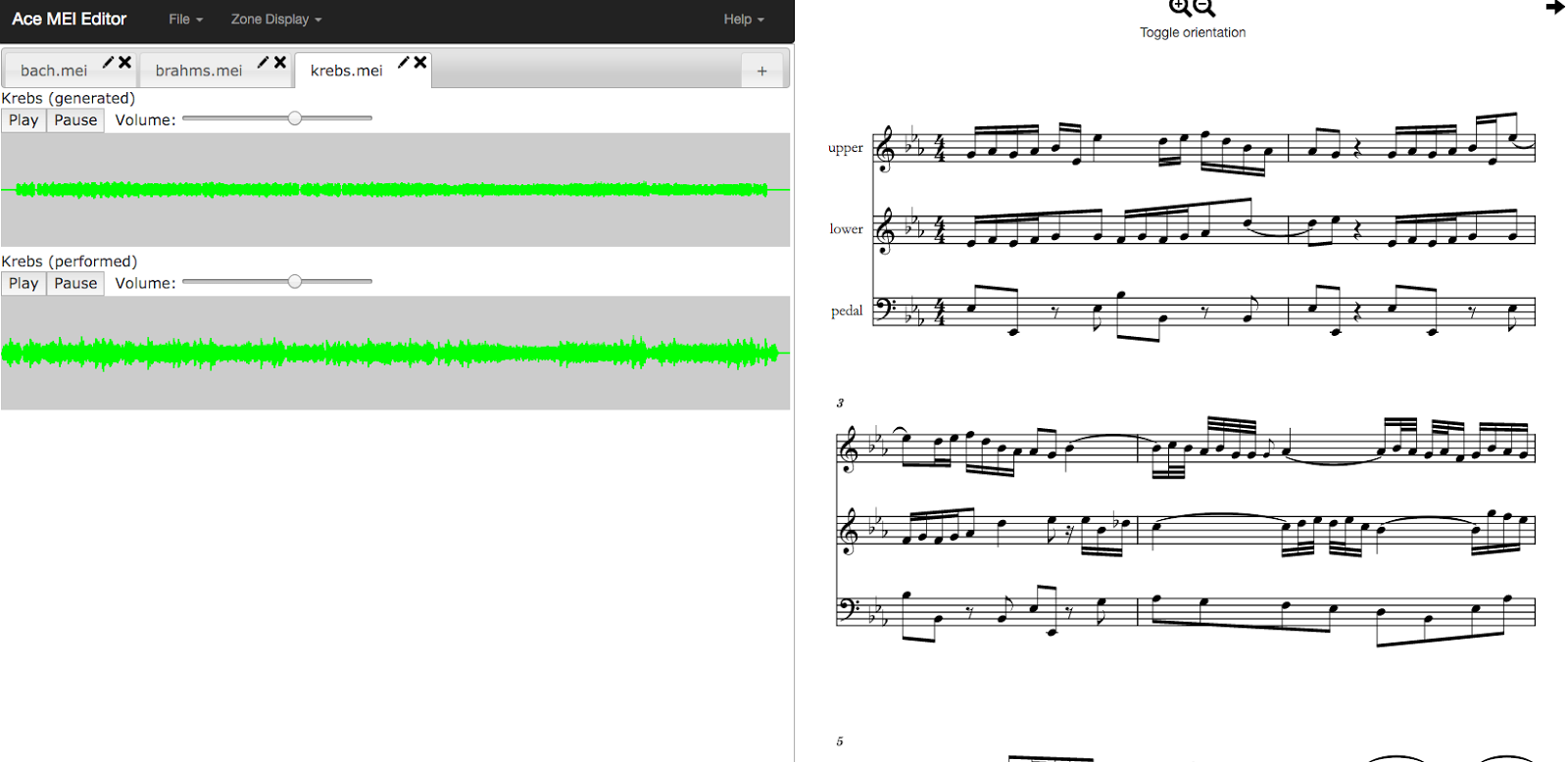
- Musical score alignment and synchronization
Verovio : This tool is rendering MEI files visually and is synchronizing music playback to score highlighting. Demo
- Media Annotation
EdX : This tool is used in Harvard for video playback with annotation functionalities (working over Video.JS). Together with the playback a number of additional features (timeline view, graph, transcription etc.) have been developed. Source code
Clipper is a tool for annotating and clipping time-based media. The prototype is still in development and currently there are four pilots rolled out. In Clipper a user can create virtual clips by referring to start/end times of any video; can group them to form clip lists; can form sets for particular projects; create annotations within the clips and share the work done in Clipper through a public view URL. Blog, Demo
- Digital Musical Library
Variations (visit here and here) is a digital music library client/server tool (Java/Swing). The player shows physical and logical structure of audio (e.g., multi-disc CD set) while the user can create playlists across files drop-the-needle quiz, etc.
Variations Audio Timeliner is a Java Swing tool for creating and delivering interactive annotated diagrams of musical form against sound recordings (either local or in Variations).
EVIA Ethnomusicology Video Archive is an example of hierarchical annotations/table of contents, with free text and controlled description associated with the video. User can navigate to multiple levels while the metadata editor manages controlled vocabulary fields.
Avalon media system for AV playback.The player is based on mediaelement.js and can be embedded into other web pages, can use LTI, has hierarchical table of contents. Demo
OHMS is a tool for editing/linking oral histories.
Take-Away Messages
IIIF is rapidly gaining ground in the arena of image access and photo content sharing. More than 55 organizations have adopted it and millions of items are being served through the framework. Using interoperability as a starting point, content sharing becomes easier and more fascinating. We are confident that the IxIF workshop in London can be the first step for transforming IIIF into a universal framework for audiovisual content sharing and form the basis for a new massively adopted solution.
Looking forward to the next step!
More Information
IIIF main website
IIIF blog post NISV
Community Meetings' notes
Google group discussion
IIIF GitHub